Anatomy, Pathology & Physiology Related to Gynecomastia Surgery
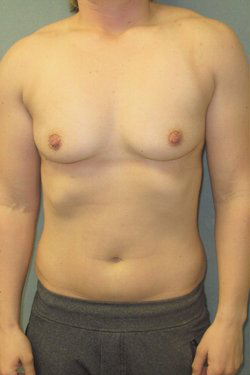
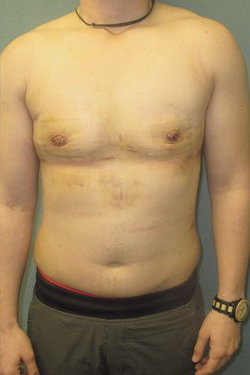
The basic structure of the male breast differs from female breast by quantity and quality of the glandular tissue. The female breast is a functional organ whose intended purpose is lactation. The male breast is a rudimentary structure that no longer has any functional purpose. The male breast is therefore an aesthetic structure.
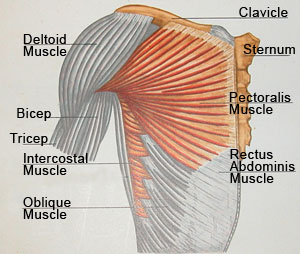
Muscle Anatomy
The ideal male breast should consist mainly of developed pectoral muscle with a minimal amount of adipose (fat) and glandular (breast) tissue. This proportion of muscle to fat and breast tissue gives the chiseled appearance.
The pectoralis muscle is a fan-shape voluntary muscle that extends from the ribs into the femur bone of the upper arm. Arm motion upwards and backwards causes movement of the pectoralis muscle. Like any voluntary muscle, the pectorals can be developed by extensive use and exercise (an example of this being bodybuilding and weight training). Doing so will give the male chest, including the areola-nipple complex, a flat shape rather than the pyramid shape that defines women’s breasts. This female breast shape is a result of large quantities of breast glandular tissue.
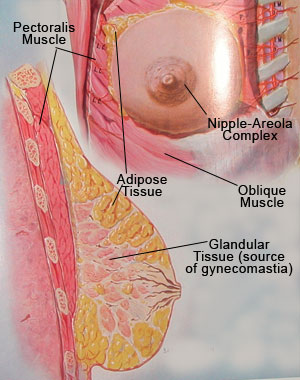
Anatomy of the Breast
Because the pectoralis muscle is the main component of the ideal male chest, the surgeon should avoid penetration into the muscle or muscle excision and should stay above the muscle fascia during any male breast reduction procedure. Any accidental penetration to the chest muscle will result in significantly increased bleeding and therefore increase the amount of scar tissue and adhesion that may manifest themselves with irregularity of the male breast skin (like dimples and lines).
The anatomy of the glandular mammary tissue is also an important factor. Usually the male breast contains small amounts of glandular tissue that are located beneath the nipple areola complex. Gynecomastia is, by definition, an increased occurrence of this gland tissue.
I have found that typically the glandular tissue extends medially, which I refer to as the head of the gynecomastia. This head is usually rounded and 0.5 to 1 inch in length. The lateral extension toward the armpit is what I refer to as the tail of the gynecomastia. This tale generally extends 1 to 2 inches laterally. While excising the glandular tissue those two extensions (the head and the tale of the gynecomastia) have to be removed in order to try to prevent recurrence of this condition.
The major bulk of the breast tissue is located under the nipple-areola complex and it varies in thickness from 0.25 to 2 inches in depth and one to five inches in diameter. The shape also may vary from oval to round to flat. In order to prevent recurrence only about one-quarter to one-third of an inch of thickness should be preserved. This sliver of glandular tissue should remain in order to prevent concavity of the breast. Ultimately, over 90%-95% of the breast tissue can be excised. Due to the low body fat level in body builders and athletes, the sliver of glandular tissue that remains after the surgery can be even thinner. Because of their well-defined pectoralis muscles, this small remnant of glandular tissue is enough to preserve the flatness of the areola and prevent concavity.
The elasticity of the skin and the thickness of subcutaneous tissue are important to the final outcome of gynecomastia surgery. There are varying degrees of skin elasticity. The important factors are:
- The patient age – the younger is, the patient the more elastic the skin
- The amount of excess skin
- The breast shape which can be saggy or tubular
Depending on the amount of excess skin and the breast shape, in same cases a skin reduction procedure may be required.
For these and others cases I have developed my own surgical technique, the Natural Blend Technique, to minimize the scar and improve the overall results. The Natural Blend Technique is a method of minimizing the scar while maximizing the excision of glandular (breast) tissue and fat. Of paramount importance is the need to excise the glandular and adipose tissue in specific locations so as to create proportional harmony and thus blend in with the rest of the chest and the body. The goal is to achieve a natural appearance of the chest.
The size of the areola is also a factor. In my experience areola reduction surgery is almost never required and in more then 90% of the gynecomastia patient the areola will contract spontaneously when the surgery is done correctly.
Nipple reduction: In some cases the nipple itself (not the larger areola) has to be reduced in length and width. I use my own technique that leaves minimal scar tissue and greatly improves the shape and size of the nipple.
Adipose tissue: Liposuction can be an important factor when performing this surgery. When it is not done uniformly it may leave indentations and irregularities in the chest. In my experience I have found that there are different varieties of adipose tissue:
- Hard – This type of adipose tissue contains more fibrous tissue and therefore is more difficult to liposuction and results in increased bleeding.
- Soft – This is usually seen in overweight people and is usually easer to liposuction and results in less bleeding.
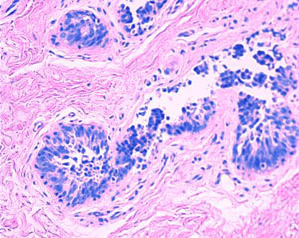
Typcial Pathology Speciman of Gynecomastia
(Benign ductal epithelial hyperplasia and mild periductal stromal edema.)
The adipose tissue is located between the pectoralis muscle fascia and the skin. In large fatty breast and in significantly over weight people, the fatty tissue may infiltrate the glandular tissue and in some cases may even infiltrate the pectoralis muscle. In many of these cases the adipose tissue may also infiltrate the armpits and therefore liposuction of the armpits may be beneficial.
The glandular tissue can be easily distinguished from the adipose tissue by its white glistering color versus the yellowish color of the fatty tissue. All glandular tissue removed from the breast during surgery is sent to a pathology laboratory for examination to confirm the benign nature of the tissue.
All of the above factors of the anatomy, pathology, and physiology of the individual patient will influence the choice of strategy in remedying this condition and the outcome of surgery.